Given a Bayesian network, d-Separation presents a way to check if a set of variables, ![]() , is conditionally independent of another set of variables,
, is conditionally independent of another set of variables, ![]() , given an observed set of variables
, given an observed set of variables ![]() . The observed set is also called the evidence. In this article, the conditional independence of two single nodes
. The observed set is also called the evidence. In this article, the conditional independence of two single nodes ![]() and
and ![]() given
given ![]() is explored. This can be extended to sets. Two sets are conditionally independent if each element of the first set is conditionally independent of every element in the second set.
is explored. This can be extended to sets. Two sets are conditionally independent if each element of the first set is conditionally independent of every element in the second set.
Reachability
Dependence is associated when there exists an active path connecting the two nodes. If there is no active path between the two nodes, they are said to be separated. Whether a path is active depends on the direction of the edges between the nodes and which nodes are part of the evidence ![]() . Hence, the term d-Separation.
. Hence, the term d-Separation.
Two nodes ![]() and
and ![]() are conditionally independent given evidence
are conditionally independent given evidence ![]() , if
, if ![]() and
and ![]() are d-separated by
are d-separated by ![]() . This holds true when all undirected paths between
. This holds true when all undirected paths between ![]() and
and ![]() are inactive. The direction of the arrows in the path can fall into one of
are inactive. The direction of the arrows in the path can fall into one of ![]() cases.
cases.
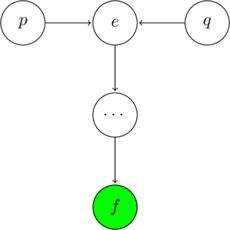
Causal Chain
If ![]() is observed, the triple
is observed, the triple ![]() is considered inactive. If
is considered inactive. If ![]() is unobserved, the triple
is unobserved, the triple ![]() is considered active.
is considered active.
| Triple | Evidence | Status |
| Inactive | |
| Active |
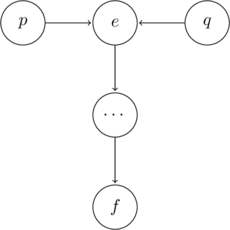
Common Cause
If ![]() is observed, the triple
is observed, the triple ![]() is considered inactive. If
is considered inactive. If ![]() is unobserved, the triple
is unobserved, the triple ![]() is considered active.
is considered active.
| Triple | Evidence | Status |
| Inactive | |
| Active |
Common Effect
If ![]() or any descendant of
or any descendant of ![]() is observed, the triple
is observed, the triple ![]() is considered active. Otherwise, the triple
is considered active. Otherwise, the triple ![]() is considered inactive.
is considered inactive.
| Triple | Evidence | Status |
| Active | |
| Active | |
| and all descendants of | Inactive |
d-Separation
- Given query: is
 conditionally independent of
conditionally independent of  , given evidence set
, given evidence set  .
. - Mark all the nodes in the evidence set.
- For all undirected non-looping paths between
 and
and 
- Check whether the path is active. A path is active if each triple along the path is active.
- If a path is active, it is not guaranteed that
 is conditionally independent of
is conditionally independent of  given
given  .
.
- All paths between
 and
and  have been found inactive. It is guaranteed that
have been found inactive. It is guaranteed that  is conditionally independent of
is conditionally independent of  given
given  .
.
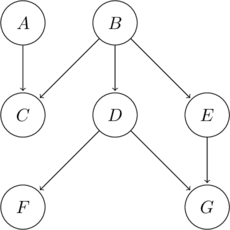
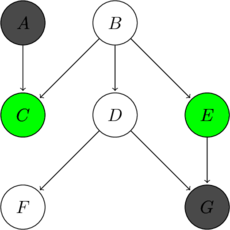
Example Network
Consider the following Bayesian Network
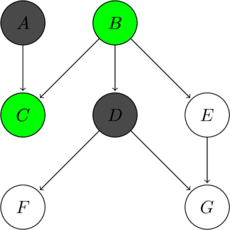
Is  conditionally independent of
conditionally independent of  given
given  ?
?
| Path | Triple | Type | Observation | Triple Status | Path Status |
| Common Effect | Active | ||||
| Common Cause | Active | ||||
| Active |
One path connecting ![]() and
and ![]() is active. Thus, it is not guaranteed that
is active. Thus, it is not guaranteed that ![]() is conditionally independent of
is conditionally independent of ![]() given
given ![]() .
.
Is  conditionally independent of
conditionally independent of  given
given  ?
?
| Path | Triple | Type | Observation | Triple Status | Path Status |
| Common Effect | Active | ||||
| Common Cause | Inactive | ||||
| Inactive |
All paths connecting ![]() and
and ![]() are inactive. Thus, it is guaranteed that
are inactive. Thus, it is guaranteed that ![]() is conditionally independent of
is conditionally independent of ![]() given
given ![]() .
.
Is  conditionally independent of
conditionally independent of 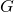 given
given  ?
?
| Path | Triple | Type | Observation | Triple Status | Path Status |
| Common Effect | Active | ||||
| Common Cause | Active | ||||
| Causal Chain | Inactive | ||||
| Inactive | |||||
| Common Effect | Active | ||||
| Common Cause | Active | ||||
| Causal Chain | Active | ||||
| Active |
One path connecting ![]() and
and ![]() is active. Thus, it is not guaranteed that
is active. Thus, it is not guaranteed that ![]() is conditionally independent of
is conditionally independent of ![]() given
given ![]() .
.